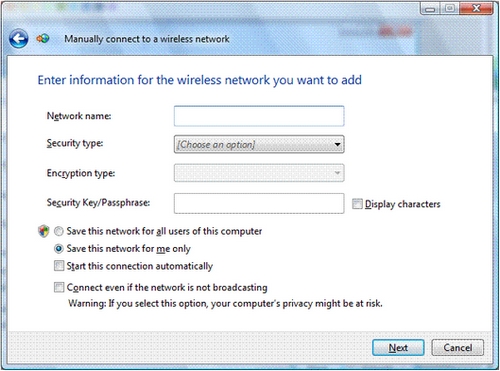

| Security type. The choices are the following: • No authentication (Open) Open system authentication with no encryption. • WEP Open system authentication with Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). • WPA-Personal Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) with a preshared key (also known as a passphrase). • WPA-Enterprise WPA with IEEE 802.1X authentication. • WPA2-Personal WPA2 with a preshared key. • WPA2-Enterprise WPA with IEEE 802.1X authentication. • 802.1x IEEE 802.1X authentication with WEP (also known as dynamic WEP). NOTE: The choices listed depend on the capabilities of your wireless network adapter that are reported to Windows. |
| The shared key authentication method is not listed. Microsoft strongly discourages its use because it provides weak security for your wireless network. To configure shared key authentication, select No authentication (Open) here and then select Shared from the Security tab in the properties of the wireless network (described later in this article). |
| Encryption type. The choices depend on the selected security type. The three encryption types are WEP (128-bit), Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) (128-bit), and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) (128-bit). • When the No authentication (Open) security type is selected, None is selected. • When the WEP security type is selected, WEP is selected. • When the WPA-Personal security type is selected, you can select TKIP or AES. • When the WPA-Enterprise security type is selected, you can select TKIP or AES. • When the WPA2-Personal security type is selected, you can select TKIP or AES. • When the WPA2-Enterprise security type is selected, you can select TKIP or AES. • When the WEP (802.1x) security type is selected, WEP is selected. NOTE: The choices listed depend on the capabilities of your wireless network adapter that are reported to Windows. |